- ASIC
- 电池管理 IC
- 时钟和时序解决方案
- ESD 和浪涌保护器件
- 汽车以太网
- 评估板
- 高可靠性
- 隔离
- 存储器
- 微控制器
- 功率产品
- 射频
- 安全智能卡解决方案
- 传感器技术
- 小信号晶体管和二极管
- 收发器
- 通用串行总线(USB)
- 无线连接
- 英飞凌大中华区生态圈
- 搜索工具
- 技术
- 封装
- 购买渠道
- 概览
- 嵌入式闪存eFlash IP 解决方案
- RAM和Flash多芯片封装MCP解决方案
- F-RAM铁电存储器
- NOR 闪存
- nvsRAM非易失性存储器
- PSRAM伪静态随机存储器
- 抗辐射和高可靠性的存储器
- RRAM阻变存储器
- SRAM静态随机存储器
- 晶圆和裸片存储器解决方案
- 概览
- AC-DC电源转换
- 电动汽车动力系统
- D 类音频放大器 IC
- 非接触式电源和检测 IC
- DC-DC 转换器
- 二极管&晶闸管 (Si/SiC)
- 氮化镓(GaN)
- GaN EiceDRIVER™高速栅极驱动器
- IGBT 产品及驱动器件
- 智能功率模块(IPM)
- LED 驱动芯片
- 电机控制 IC 和驱动
- 高效能功率MOSFET 和 MOS管
- 功率模块
- 电源模块
- 保护和监控IC
- 碳化硅 (SiC)
- 智能电源开关
- 固态继电器
- 无线充电 IC
- 概览
- Calypso® 产品
- CIPURSE™ 产品
- 非接触式存储
- 了解 OPTIGA™ 嵌入式加密解决方案
- SECORA™ 安全解决方案
- 安全控制器
- 智能卡模块
- 政府身份证的智能解决方案
- 概览
- REAL3™ 3D ToF 图像传感器
- MOTIX™ MCU (SoC) 基于 Arm® Cortex®-M0,集成半桥驱动器
- 气体传感器
- Inductive position sensors
- 微机电系统麦克风
- 压力传感器
- 雷达传感器
- 磁性位置传感器
- 磁性速度传感器
- 概览
- USB 2.0 外设控制器
- USB 3.2 外设控制器
- USB 集线器控制器
- USB PD 高压微控制器
- USB-C AC-DC 和 DC-DC 充电解决方案
- USB-C 充电端口控制器
- USB-C 供电控制器
- 概览
- AIROC™ 车载无线
- AIROC™ 蓝牙Bluetooth® 和多协议解决方案
- AIROC™ 互联微控制器
- AIROC™ Wi-Fi + Bluetooth® 组合
- 概览
- FM0+ 32 位 Arm® Cortex-M0®+ 微控制器 (MCU) 系列
-
FM3 32 位 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU) 系列
- 概览
- FM3 CY9AFx1xK 系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx1xL/M/N 系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx2xK/L 系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx3xK/L 系列超低漏电流 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx4xL/M/N 系列低功耗 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFx5xM/N/R 系列低功耗 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9AFxAxL/M/N 系列超低漏电流 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx1xN/R 高性能系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx1xS/T 高性能系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx2xJ 系列 Arm® Cortex-M3®微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx2xK/L/M 系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM3 CY9BFx2xS/T 系列 Arm® Cortex-M3® 微控制器 (MCU)
- FM4 32 位 Arm® Cortex-M4® 微控制器 (MCU) 系列
- 概览
-
TriCore™ AURIX™ TC2x安全模块
- 概览
- AURIX™系列 – TC21xL
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC21xSC (无线充电)
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC22xL
- AURIX™系列 – TC23xL
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC23xLA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC23xLX
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC264DA (ADAS)
- AURIX™系列 – TC26xD
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC27xT
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC297TA (ADAS)
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC29xT
- AURIX™ 系列 – TC29xTT (ADAS)
- AURIX™系列 – TC29xTX
- AURIX™ TC2x仿真器件
- 32 位TriCore™ AURIX™ – TC3x
- 32 位TriCore™ AURIX™ - TC4x
- 概览
- PSoC™ 4 Arm® Cortex® -M0/M0+
- PSoC™ 4 HV Arm® Cortex® -M0+
- PSoC™ 5 LP Arm® Cortex® -M3
- PSOC™ 6 Arm® Cortex-M4®/M0+
- PSOC™ Multitouch Arm® Cortex®-M0
- 32 位 PSOC ™ Control Arm® Cortex ® -M33 MCU
- PSOC™ Fingerprint Arm® Cortex®-M0+
- PSOC™ Automotive 4: Arm® Cortex®-M0/M0+
- PSoC™ Edge Arm® Cortex® M55/M33
- 概览
- 32 位 TRAVEO™ T2G Arm® Cortex®用于车身电子应用
- 用于仪表盘的 32 位 TRAVEO™ T2G Arm® Cortex®
- 概览
- 32 位XMC1000工业微控制器 Arm® Cortex-M0®
- 32 位XMC4000工业微控制器 Arm® Cortex-M4®
- XMC5000 Industrial Microcontroller Arm® Cortex®-M4F
- 32 位XMC7000工业微控制器 Arm® Cortex-M7®
- 概览
- 桥式整流器和交流开关
- CoolSiC™ 肖特基二极管
- 二极管裸片
- 硅二极管
- 晶闸管/二极管模块
- 晶闸管软启动器模块
- 晶闸管/二极管盘
- 概览
- 32-bit PSOC™ Control Arm® Cortex®-M33 MCU
- iMOTION™集成电机控制解决方案
- Embedded Power ICs (System-on-Chip) -146
- MOTIX™电机控制IC用于BLDC电机
- MOTIX™ 电机控制IC,用于有刷直流电机
- MOTIX™ 多半桥IC用于伺服和步进电机
- 概览
- 汽车级MOSFET
- 双 MOSFET
- MOSFET(Si 和 SiC)模块
- N 沟道耗尽型 MOSFET
- N沟道MOS管
- P沟道MOS管- 功率MOSFET
- 碳化硅 CoolSiC™ MOSFET
- 250V至600V G14小信号MOS
- 概览
- OPTIGA™ Authenticate
- OPTIGA™ Authenticate NFC 解决方案
- OPTIGA™ Connect – 交钥匙式 eSIM 安全解决方案
- OPTIGA™ Trust
- OPTIGA™ 可信平台模块 (TPM)
- 概览
- EZ-PD™ ACG1F 单端口 USB-C 控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG2 USB Type-C 端口控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG3PA Automotive USB-C 和 Power Delivery 控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG4 双端口 USB-C 和 PD
- EZ-PD™ CCG5 双端口和 CCG5C 单端口 USB-C PD 控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG6 单端口 USB-C & PD 控制器
- EZ-PD ™ CCG6_CFP 和 EZ-PD ™ CCG8_CFP 双单端口 USB-C PD
- EZ-PD™ CCG6DF 双端口和 CCG6SF 单端口 USB-C PD 控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG7D 汽车双口 USB-C PD + DC-DC 控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG7S 汽车单口 USB-C PD 解决方案,配备DC-DC控制器
- EZ-PD™ CCG7SAF 车规级单端口 USB-C PD + DC-DC 控制器 + FETs
- EZ-PD™ CCG8 双/单口 USB-C PD
- EZ-PD™ CMG1 USB-C EMCA 控制器
- 支持 EPR 的 EZ-PD™ CMG2 USB-C EMCA 控制器
- 最新动态
- 航空航天
- 智能汽车解决方案
- 消费类电子产品
- 健康和 生活方式
- 家用电器
- 工业
- 信息和通信技术
- 可再生能源
- 机器人
- 安全解决方案
- 智能家居和楼宇
- 解决方案
- 概览
- 适配器和充电器
- 适用于智能电视的完整系统解决方案
- 移动设备和智能手机解决方案
- 多旋翼飞机和无人机
- 电动工具
- 家庭娱乐应用的半导体解决方案
- 智能会议系统
- 概览
- 汽车辅助系统
- 车载网关
- 汽车配电系统
- 车身控制模块 (BCM)
- 舒适便捷电子产品
- 区域 DC-DC 转换器 48 V-12 V
- 区域控制器
- 概览
- 汽车车载主机
- 汽车 USB-C 电源和数据解决方案
- 汽车仪表盘
- 汽车远程信息处理控制单元 (TCU)
- 中央信息显示屏(CID)
- 高性能驾驶舱控制器
- 舱内无线充电
- 智能仪表盘(电动两轮车和三轮车)
- 最新动态
- 概览
- AIROC™ 软件&工具
- AURIX™应用软件
- DRIVECORE 用于汽车软件开发
- iMOTION™ 工具和软件
- Infineon智能功率开关和栅极驱动器工具套件
- MOTIX 软件&工具
- OPTIGA™工具和软件
- PSOC™ 软件&工具
- TRAVEO™ 软件&工具
- XENSIV™ 工具和软件
- XMC™ 工具和软件
- 概览
- EZ-PD™ CCGx Dock 软件开发工具包
- FMx Softune IDE
- ModusToolbox™ 软件
- PSOC™ Creator软件
- 雷达开发套件
- 锈
- USB 集线器控制器
- 无线连接蓝牙网状网络辅助应用程序
- XMC™ DAVE™ 软件
- 最新动态
- 支持
- 培训
- 英飞凌开发者社区
- 最新消息
商业财经新闻
16/12/2025
商业财经新闻
08/12/2025
商业财经新闻
04/12/2025
商业财经新闻
03/12/2025
- 公司名称
- 我们的故事
- 活动资讯
- 新闻中心
- 投资者
- 职业生涯
- 质量
- 最新消息
商业财经新闻
16/12/2025
商业财经新闻
08/12/2025
商业财经新闻
04/12/2025
商业财经新闻
03/12/2025
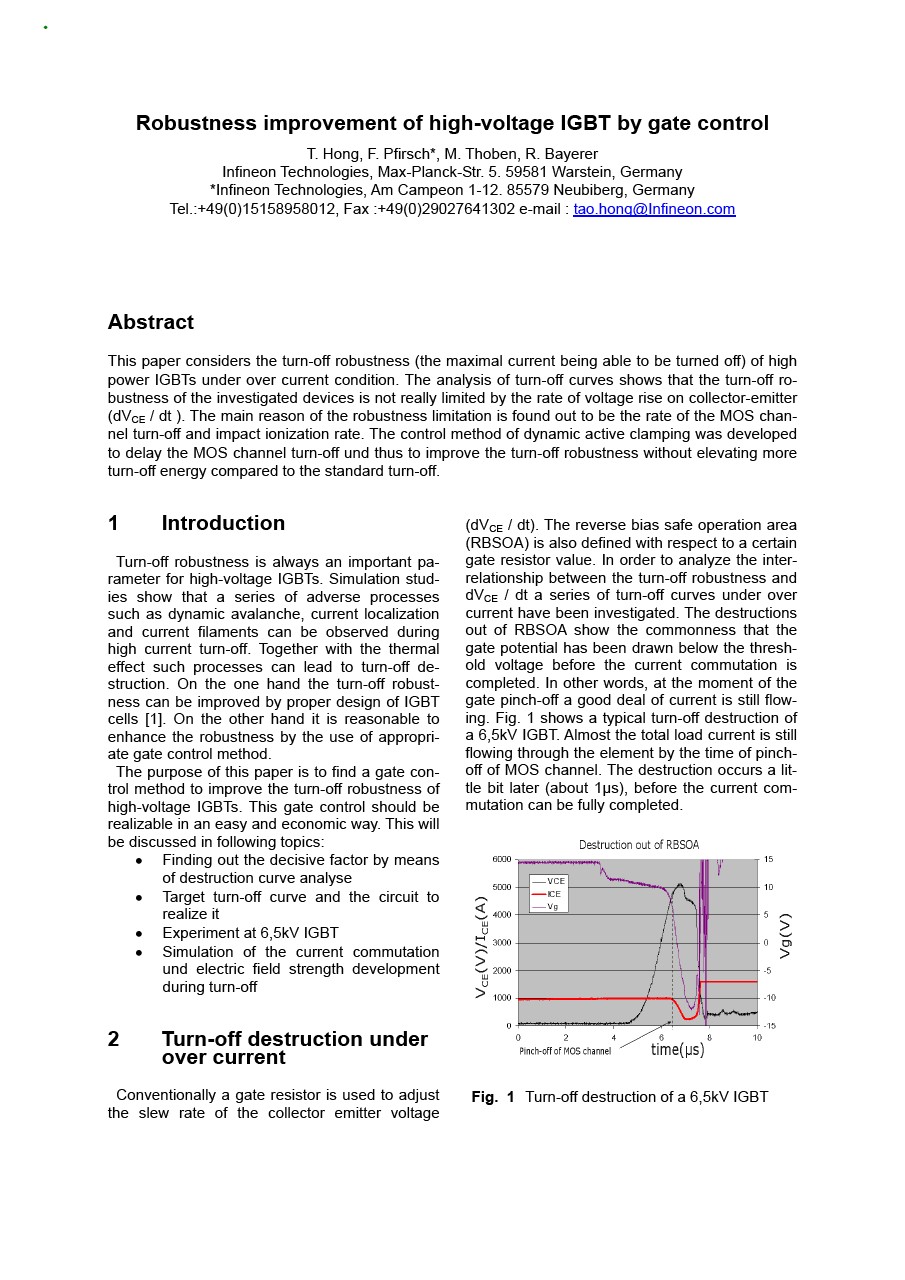
Robustness improvement of high-voltage IGBT by gate control
This paper considers the turn-off robustness (the maximal current being able to be turned off) of high power IGBTs under over current condition. The analysis of turn-off curves shows that the turn-off robustness of the investigated devices is not really limited by the rate of voltage rise on collector-emitter (dVCE / dt ). The main reason of the robustness limitation is found out to be the rate of the MOS channel turn-off and impact ionization rate. The control method of dynamic active clamping was developed to delay the MOS channel turn-off und thus to improve the turn-off robustness without elevating more turn-off energy compared to the standard turn-off. Turn-off robustness is always an important parameter for high-voltage IGBTs. Simulation studies show that a series of adverse processes such as dynamic avalanche, current localization and current filaments can be observed during high current turn-off. Together with the thermal effect such processes can lead to turn-off destruction. On the one hand the turn-off robustness can be improved by proper design of IGBT cells. On the other hand it is reasonable to enhance the robustness by the use of appropriate gate control method.
注册获取更多!! 注册